Laser Doppler
Flowmetry
This is a non invasive, objective, painless,
semi-quantitative method, which is more reliable in measuring the blood flow to
the pulp. As it doesn’t cause any noxious stimuli, apprehensive or distressed, patients
accept it more readily than the current methods to assess the pulp vitality.
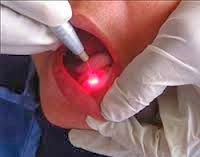
Laser light is transmitted to the pulp by means of a fiber optic probe. Laser
Doppler flowmetry uses Helium Neon (HeNe) and Gallium Aluminum ( Ga AlAs) as
semiconductor diode lasers at a power of 1 to 2 mW. The wave length of the HeNe
laser is 632.8nm and that of the semiconductor diode laser is 780 to 820nm
The scattered light from the moving red blood cells in the
circulation will be frequency-shifted, while those from the static tissues remain
unshifted. The reflected light composed of Doppler shifted and unshifted light
is returned by the afferent fibers and a signal is produced. This technique can
be successfully employed for estimating the vitality of the pulp in both adults
and children. The tooth to be checked should be isolated. The closer the probe is
positioned to the gingival margins, the higher the signal output because of the
greater volume of the pulp tissue .At the same time, the potential gingival
contamination is also higher. The ideal position to place the probe is 2 to 3
mm from the gingival margin
Different ranges of band width can be set to filter the
reflected signal, with a wider frequency being more sensitive to the moving red
blood cells with a wider range of velocity .Theoretically, a wider bandwidth such
as 15kHz is preferred, but in case of pulp vitality testing, a much narrower 3
kHz bandwidth may be ideal The end of the LDF which contacts the tooth contains
both sending and receiving optic fibers, with one of the configuration being
one source and two detectors in a triangular arrangement at the probe end
Calibration of the probes is important to ensure accurate readings .
The larger the optical fiber separation distance on the
probe, the higher the signal output as a larger surface area is covered, and
also there is potentially a higher chance of blood flow signal contamination of
the non pulp sources. To date, the 0.5mm or 0.25mm separation distances seem to
be preferred in experiments. Due to the pulsatile nature of the blood flow,
many studies.... have observed that the LDF recordings in the teeth with an
intact pulp blood flow have rhythmic fluctuations or oscillations. In teeth
without pulp blood flow, however, usually only irregular fluctuations can be
observed in contrast to the concurrent ECG readings.




.jpg)

.jpg)











.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)























